Shortage of nurses and how to offset its negative impact on hospital finances
Shortage of medical staff, especially nurses, is currently one of the most pressing issues healthcare organizations across Europe have to face.
Besides the obvious negative impacts such as insufficient patient care, this problem affects the financial health of both, private and public organizations.
However, there are several approaches that healthcare organizations can leverage to confront the nurse shortage.
The reality of the nursing workforce crisis in Europe
Europe’s health systems are in the midst of a nursing workforce crisis. Poor working conditions, low pay, high workloads and lack of career opportunities are impacting the wellbeing and satisfaction of nurses across Europe.
The COVID-19 pandemic exacerbated these challenges, leading nurses to quit or consider quitting in unprecedented numbers. To add to that, an aging population, coupled with increasingly complex care needs (widespread chronic diseases, changes in lifestyle patterns) and fiscal constraints have impacts on the sustainability of the healthcare sector in the long term.
While research shows that shortages of doctors could be contained, the understaffing of the nursing profession is a very serious issue affecting health indicators such as mortality, morbidity and safety. For each 10% increase in the number of nurses, the mortality rate of a hospitalized patient decreases by 10%.
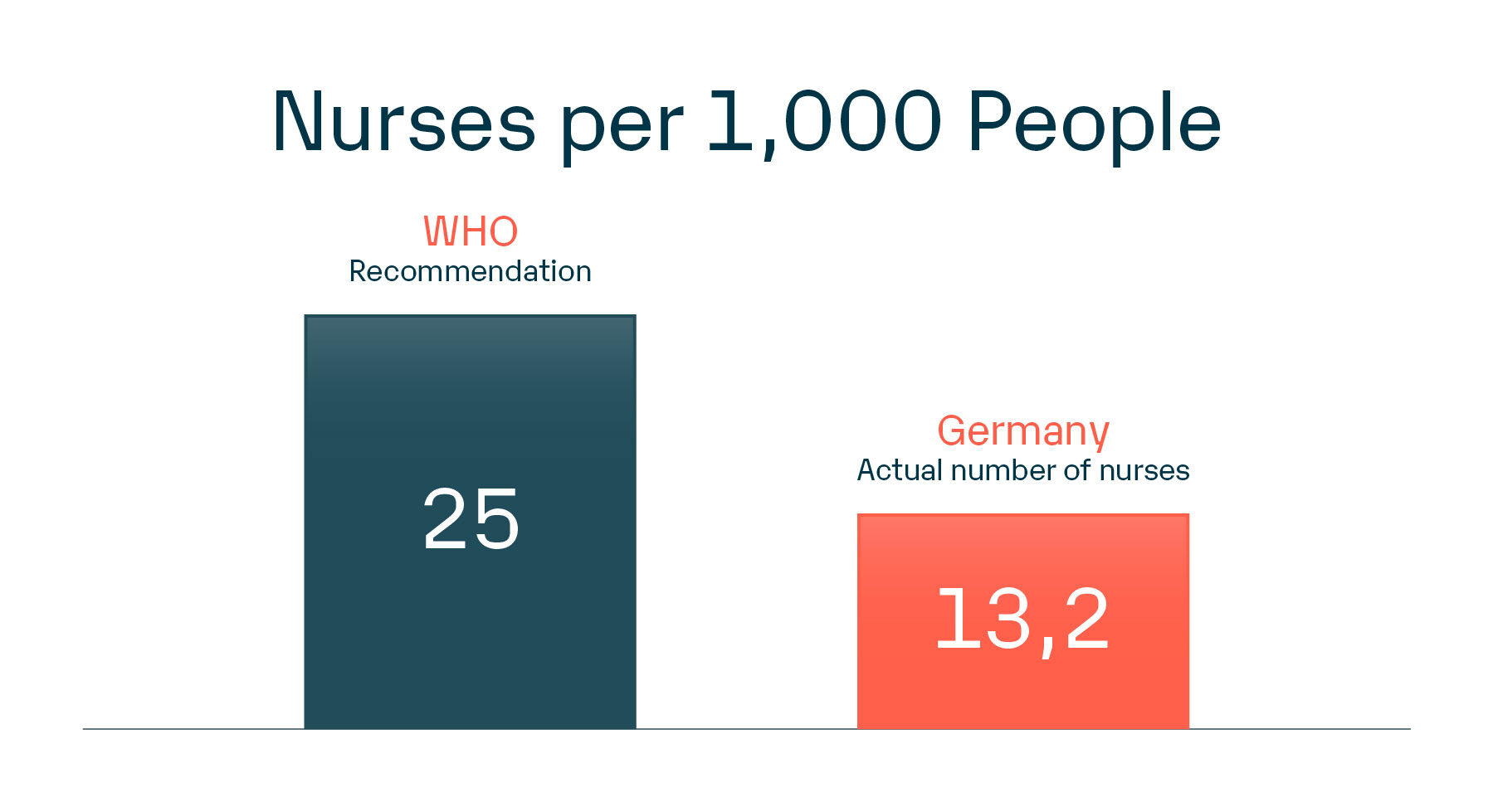
In several countries, nurse-to-population ratios fall far below the recommended minimum standards. For instance, Germany currently has approximately 13 nurses per 1,000 people, whereas the WHO recommends a minimum of 25 nurses per 1,000 people.

What are the economic implications for healthcare organizations?
Higher salaries
Low pay puts a strain on nurses and contributes to poor retention. In some countries – such as Finland, France, Latvia and Lithuania – nurses’ salaries are below the national average. To attract and retain nurses in the face of shortages, healthcare facilities are forced to offer competitive salaries and benefits. Higher salaries for nurses contribute to escalating labor costs, a significant component of overall healthcare expenditures.
Administrative costs and economic impact
Besides the actual salaries, healthcare organizations must invest in recruitment efforts, administrative processes, and compliance with regulations associated with nurse staffing shortages. It is estimated that nurse staffing accounts for approximately 60-70% of a hospital's total budget, underscoring the substantial financial impact of nurse shortages.

Burnout and turnover
Overworked nurses are more likely to experience burnout and leave the profession. High turnover rates incur recruitment and training costs and can also lead to inconsistent care. Replacing a registered nurse can cost between 35,000€ and 53,000€, as per data from the Nursing Solutions, Inc. National Healthcare Retention & RN Staffing Report. Moreover, the physical and mental toll on nurses contributes to higher sick leave, imposing further financial strains on healthcare facilities. A 2020 UK review of working conditions for nurses found that compared with nurses working in the private sector, public sector nurses had high levels of stress, high pressure from staff shortages and double the number of sickness days.
Nurse strikes
In the end, inadequate staffing, low salaries and poor working conditions push nursing staff to strike. These strikes have surged in recent years at an unprecedented rate. They can have a significant impact on healthcare facilities, patients, and nurses themselves. With fewer nurses available to provide care, patients may experience delays in receiving treatment, or they may not receive the level of care they need. Additionally, the loss of revenue due to canceled appointments and procedures can be devastating to the bottom line of the organizations.
Watch the video where Advisor and board member, Roman Rosenkranz, reflects on how to address the nurse shortage with digital health innovations.
What can be done to counteract the shortage of nursing staff?
Legislature
An even more worrying trend is the aging of the nursing workforce, which combined with an increased need will lead to a major shortage on the labor market. Healthcare organizations cannot offset these trends by themselves. That's where a necessity for a legislature changes rise on the national, as well as European level. Areas such as retention, good and attractive working conditions/ environment, valorisation and prevention of outflows of such workforce need to be improved.
International recruitment
Although the international recruitment of nurses is widely practiced, it is not a sustainable solution to the nursing workforce crisis. International recruitment, outside of a country’s domestic workforce, has been used as the primary short-term solution to nurse shortages, especially in Germany, Spain and the UK. But this approach leads to staff shortages in origin countries and can have negative effects on migrant nurses, such as de-skilling and the loss of time and finances due to the need to requalify in the destination country.
Innovative technology
Experts agree that until the legislature changes, innovative technologies can counteract some of the burden placed on the nursing staff.
For example, the economic implications of automating repetitive tasks in healthcare practices are profound. Automated documentation alone could save up to 1.5 hours per shift, while automatic vital sign monitoring could significantly reduce the time spent on routine checks.
This technology has the potential to decrease the occurrence of adverse events, like falls or pressure ulcers, optimize the use of hospital beds, and reduce unnecessary extended stays, thereby improving hospital revenue and operational efficiency.
Bed exit alarms are especially important and often take up to 50% of the work time per shift. Furthermore, a holistic device used for vital signs monitoring can replace multiple measurement devices currently used for every patient. In the long run, this can provide a financial benefit together with a less cluttered working environment.
Arguably, with more time on their hands, nursing staff can use their expertise for actual patient care and treatment. This might benefit the overall well-being of the staff and improve the burnout and turnover rates together with the frequent sick leaves. Overall, it seems that innovative medical devices are the most viable solution that healthcare organizations have to challenge the shortage of nurses.